Academic Project
Exa-MA WP1 - Vegetation
Objective
This academic project, part of the HiDALGO21 initiative, focuses on integrating vegetation—specifically trees—into 3D urban models to enhance thermal and energy simulations for improved building energy efficiency and indoor air quality. Conducted at Cemosis2 (Center for Modeling and Simulation, Strasbourg – CNRS spinoff) within the University of Strasbourg, the work leverages OpenStreetMap3 data and CGAL4 algorithms to generate and incorporate tree models into urban terrain meshes, with a primary focus on Strasbourg, France.
Key Components
1. Data Acquisition
Tree data was sourced from OpenStreetMap using the Overpass API and cURL5 to query nodes tagged as “natural=tree” within a specified bounding box. A configurable config.json file allows users to define parameters such as the bounding box, origin coordinates, altitude, level of detail (LOD), default height range, default genus, input building mesh, and output options.
2. Tree Library
A library of 13 tree models in .stl format was created from SketchUp’s 3D Warehouse. Additional 28 genera were categorized to match similar models for broader coverage. Visualizations of a sample of models using MeshLab:
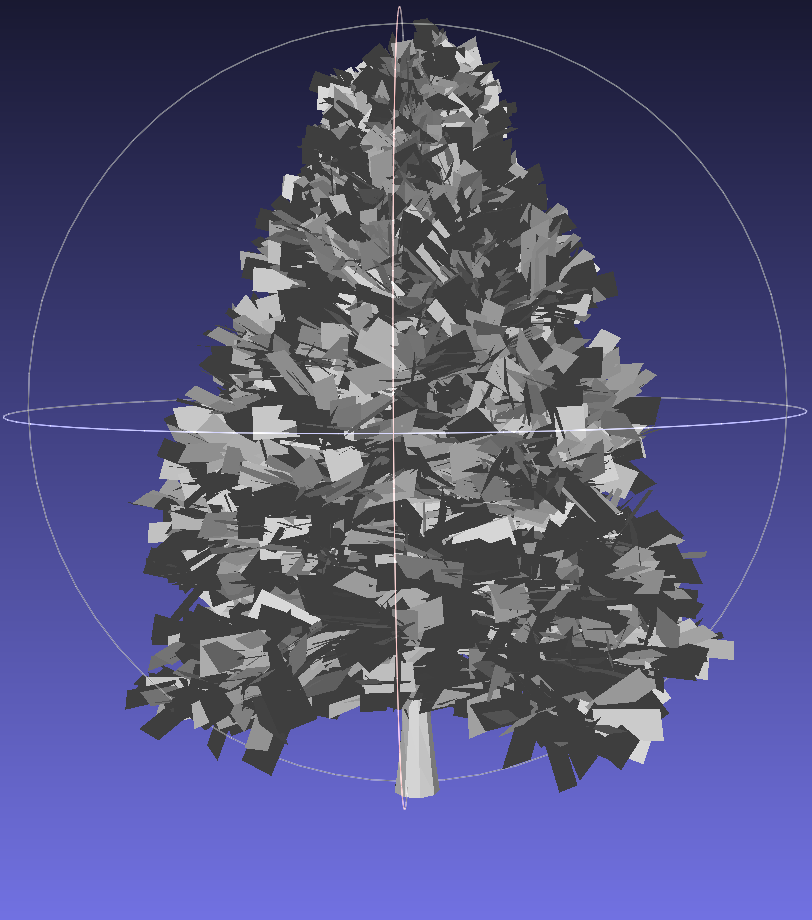
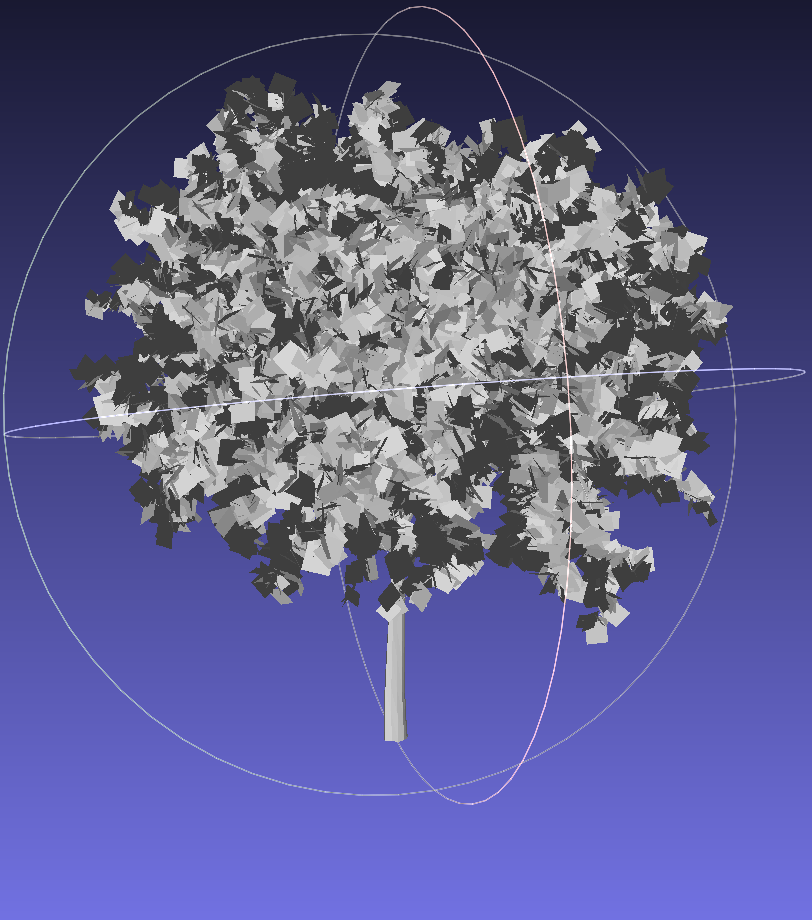
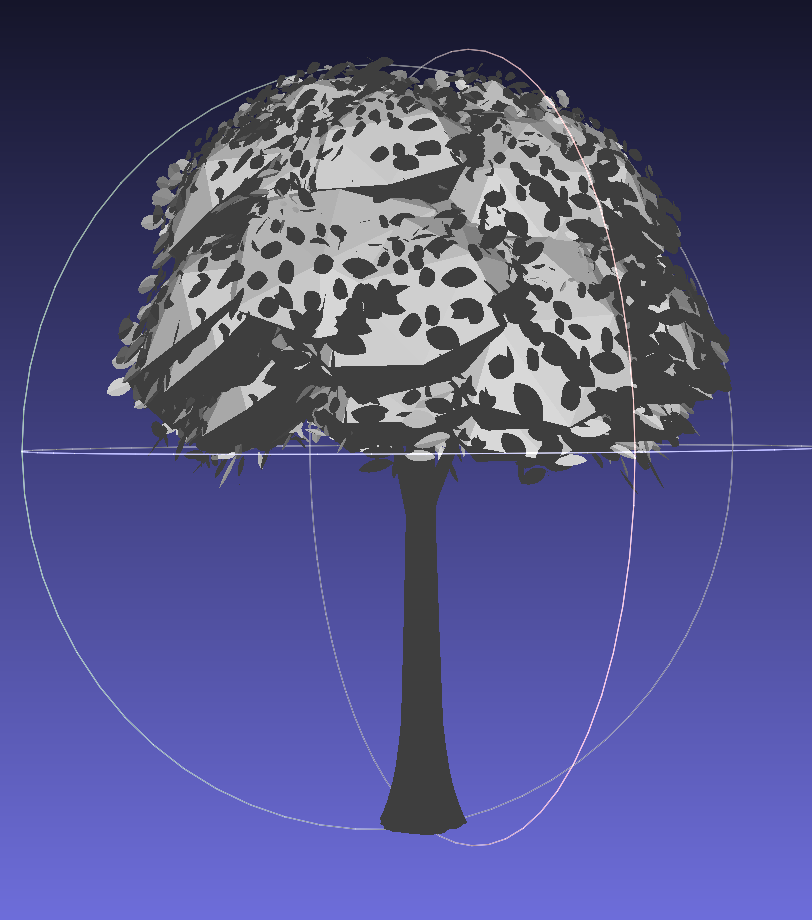
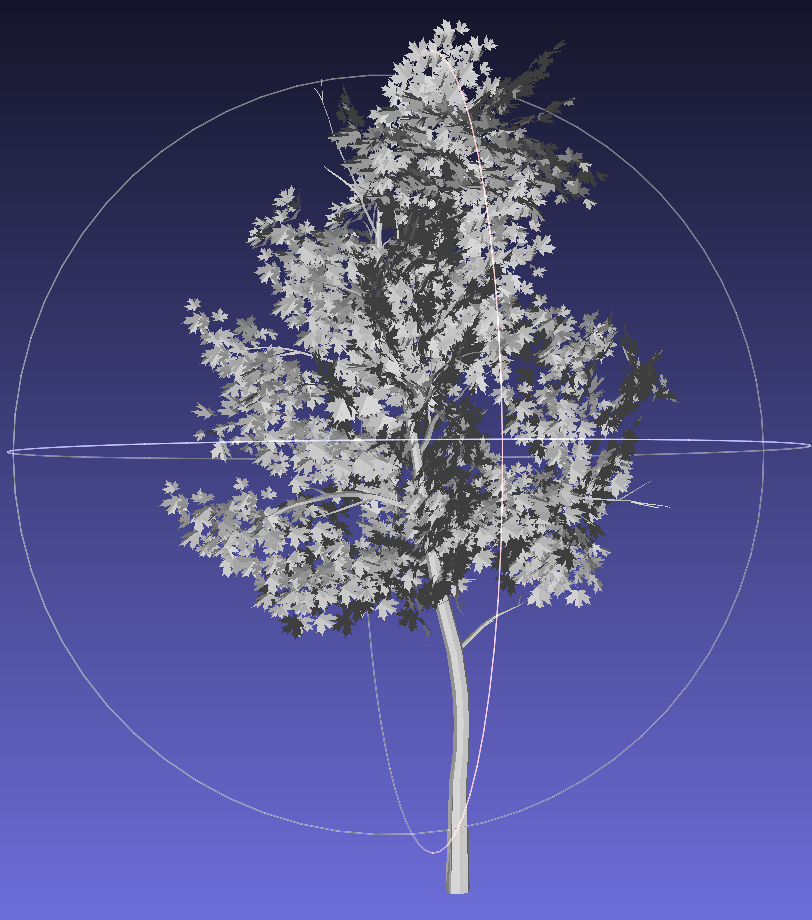
3. Dataset
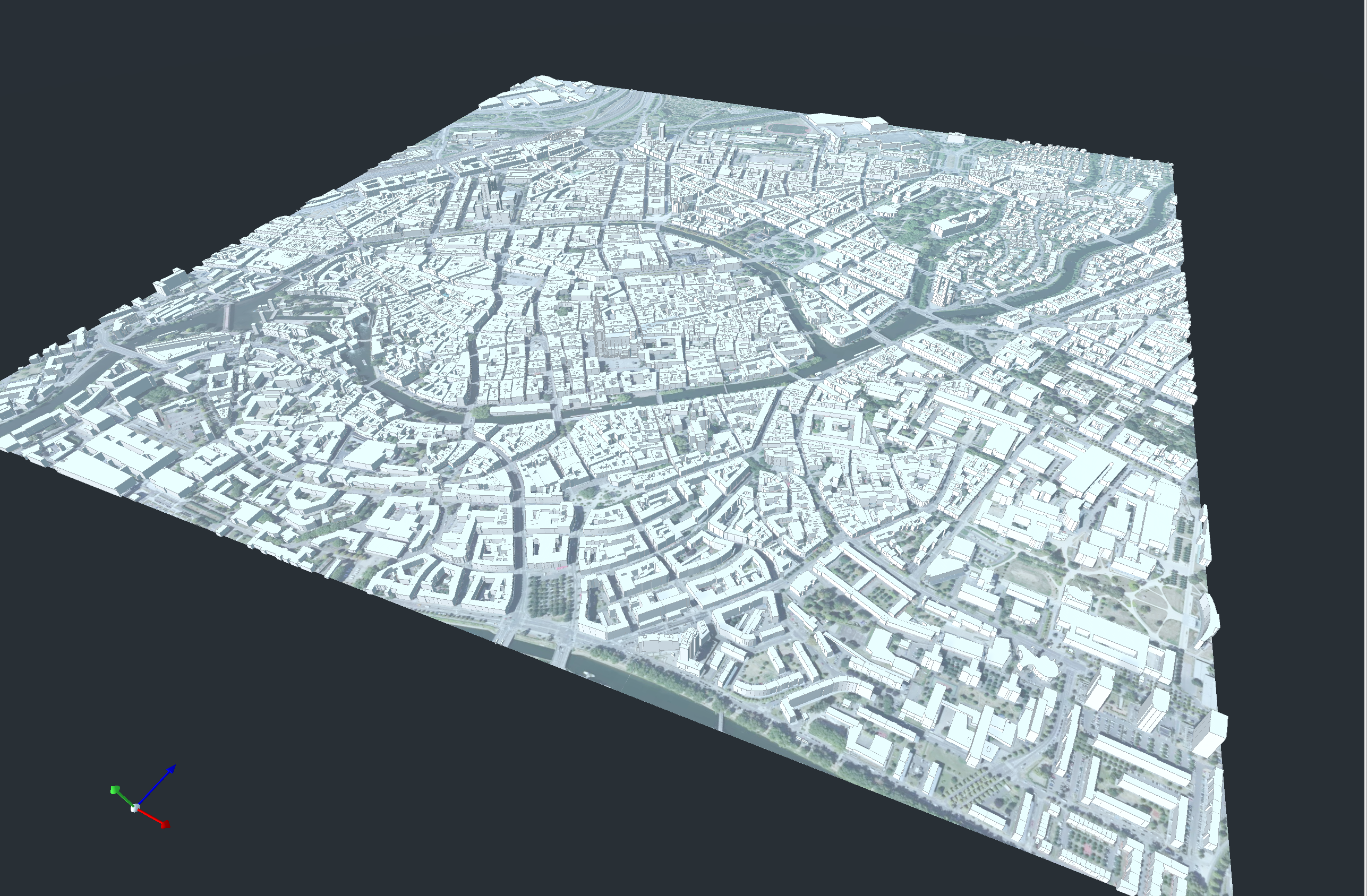
The primary dataset is a .stl file of Strasbourg’s city center, containing ~120,959 vertices and ~273,178 facets, representing terrain and buildings.
4. Alpha Wrapping
The CGAL Alpha Wrapping algorithm generates watertight meshes by shrink-wrapping a Delaunay triangulation around input data, balancing tightness and complexity with parameters alpha and offset.
5. Tree Model Generation
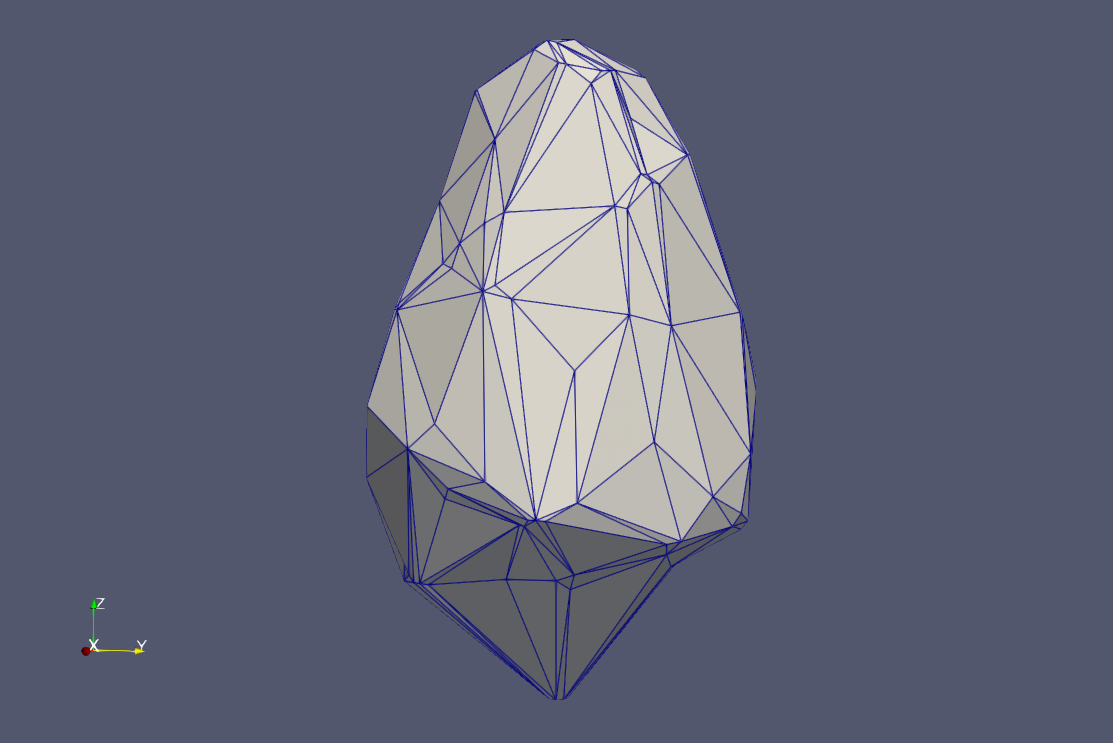
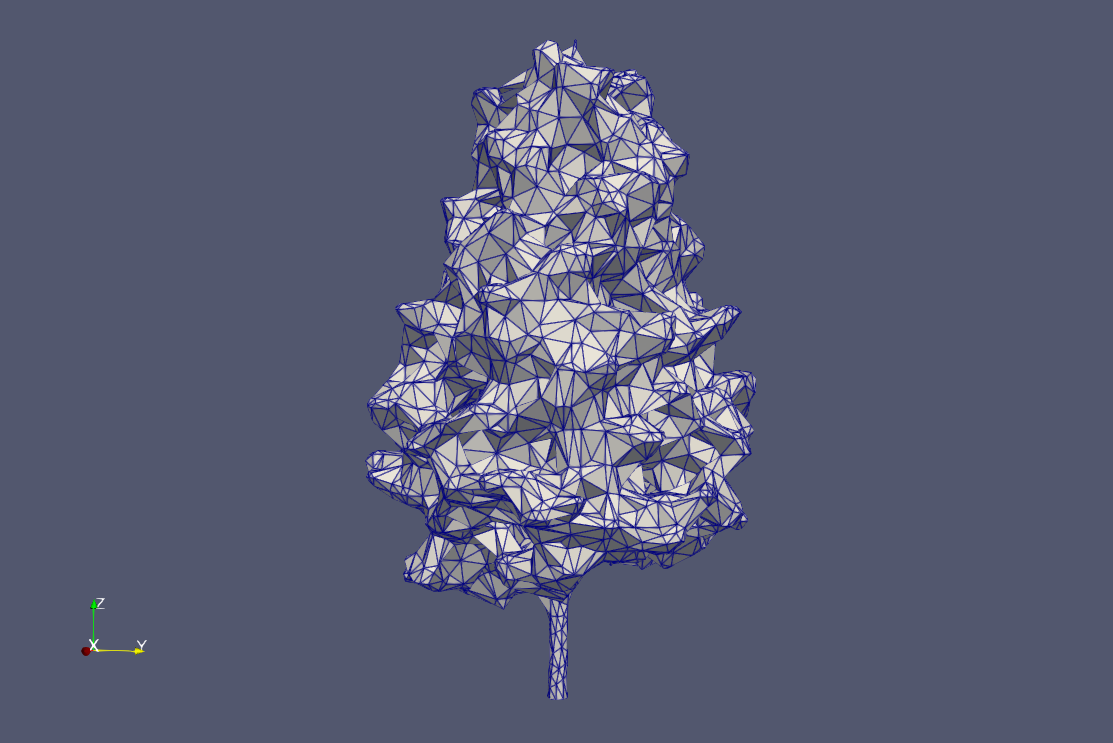
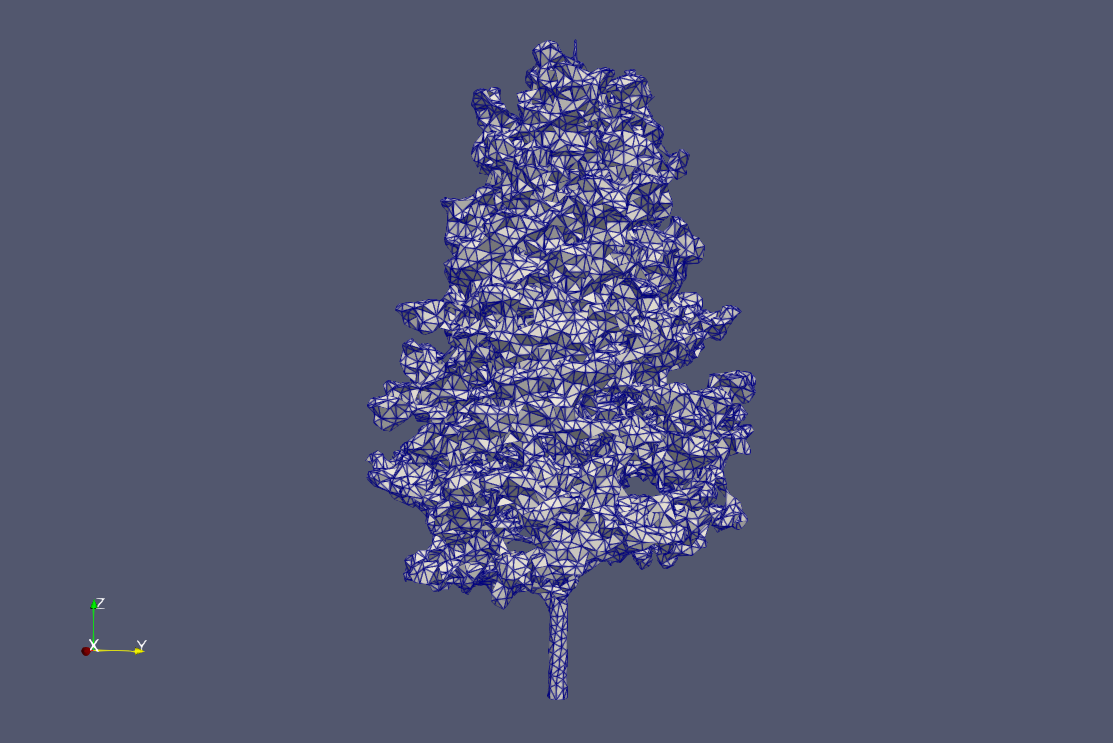
Reference meshes are pre-wrapped at LODs 0-3 (alpha: 0.1, 20, 50, 100; offset: 600). Trees are scaled and translated using CGAL Affine Transformations to match height and position.
Ginkgo examples at each LOD:

Results
Model Integration
Trees integrated into Strasbourg models, e.g., Place de la République.
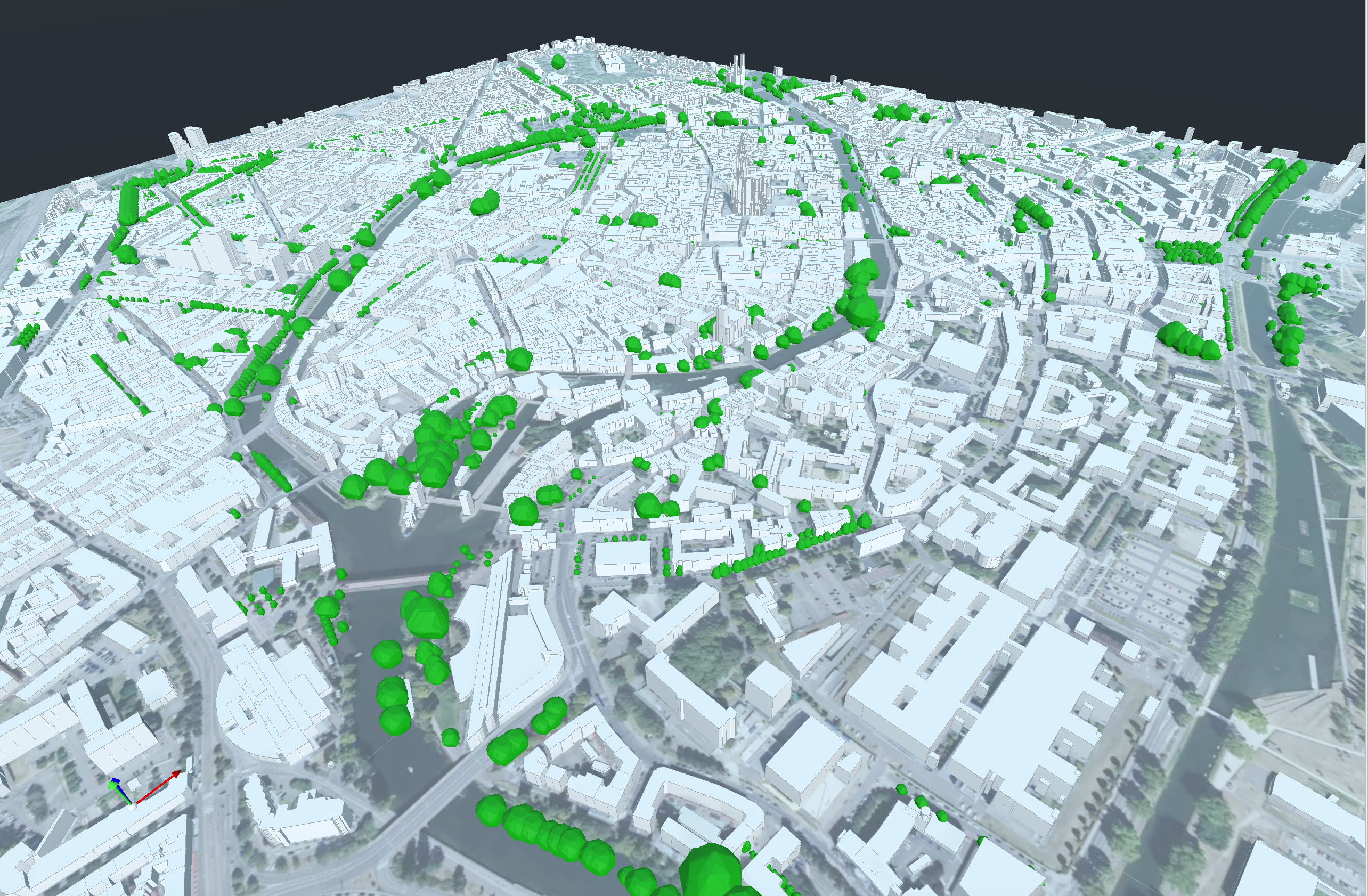
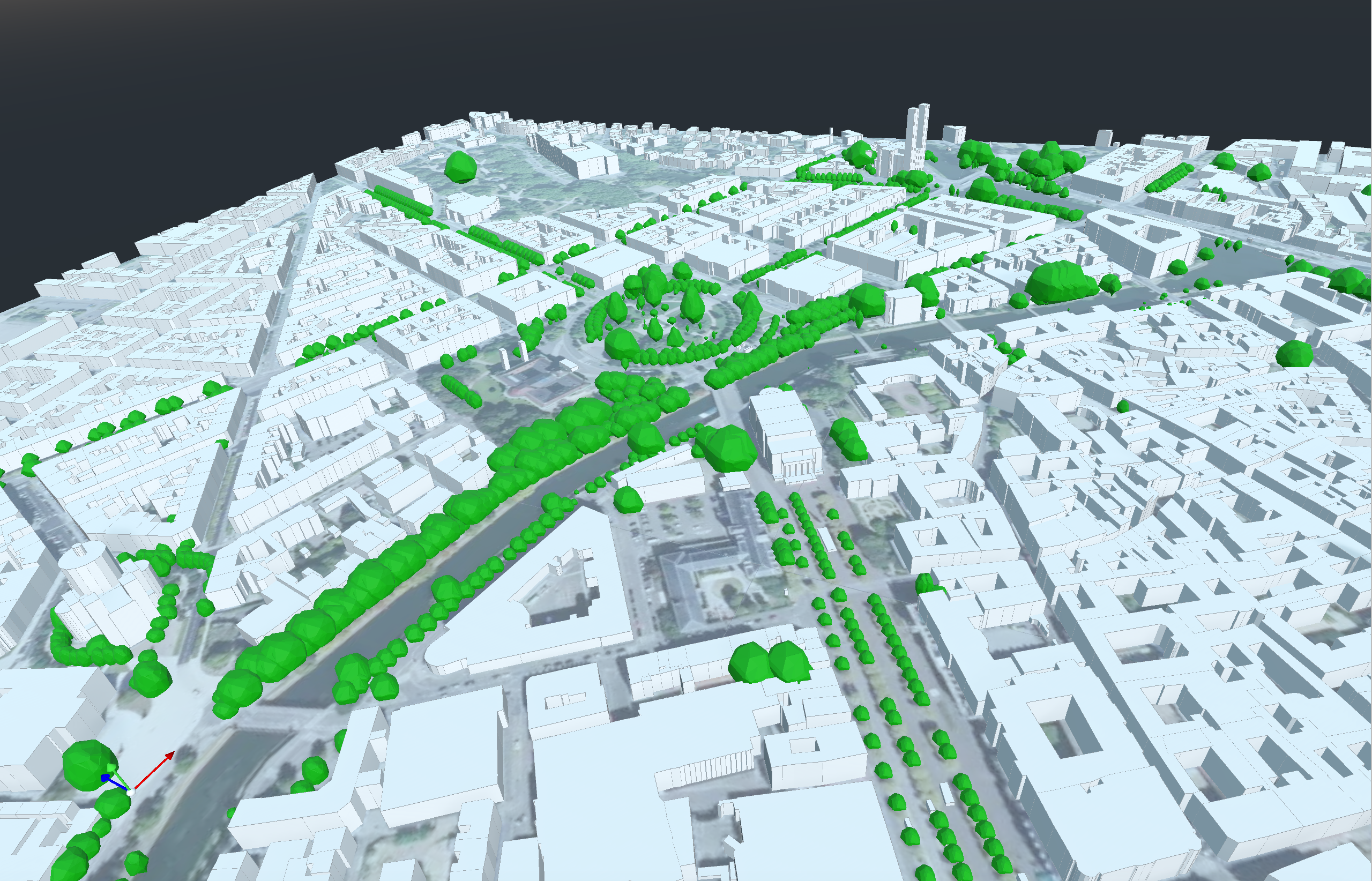
Impact and Future Work
The framework enhances urban simulations by incorporating vegetation, reducing computational complexity while maintaining realism. Future enhancements include seasonal leaf variations (clustering leaves) and shading simulations using Feel++ for PDE-based ray tracing.
Read the project report here.
References
HiDALGO2. HPC AND BIG DATA TECHNOLOGIES FOR GLOBAL CHALLENGE. 2024. Available at: HiDALGO2 ↩
Cemosis. Center for Modeling and Simulation in Strasbourg. 2024. Available at: Cemosis ↩
OpenStreetMap. OpenStreetMap Wiki. 2024. Available at: OpenStreetMap ↩
CGAL: The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library. 2024. Available at: CGAL ↩
